The protocol is one of the most fundamental aspects of a VPN connection when torrenting. It can significantly impact download speeds and reliability. OpenVPN is considered by many to be the most reliable VPN protocol for torrenting. This reputation results from its balance of security and speed.
OpenVPN supports both UDP and TCP transport layer protocols, which offer distinct advantages for torrenting. Most VPNs allow users to choose between the two, which can cause some confusion.
Understanding the differences between them lets you optimize your download experience.
The Main Differences Between UDP and TCP
Let’s break down how UDP and TCP impact your torrenting speeds and reliability.
What is TCP?
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is the workhorse of the internet. It provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked connections between applications. It operates at the transport layer, establishing a dedicated channel for data packets.
Think of it like sending registered mail; if a package is lost or arrives out of order, TCP will handle the retransmission seamlessly. This reliability makes it crucial for most web traffic but can introduce overhead that impacts P2P downloads.
What is UDP?
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) prioritizes raw speed. Also a transport layer protocol, it foregoes the connection establishment and error-correction mechanisms of TCP. Data is sent in a fire-and-forget manner (datagrams), resulting in significantly less overhead.
For torrenting, where a few missing packets won’t break the download, this translates to potentially faster transfer rates.
Key Takeaway for Torrenting
UDP usually delivers more “bang for your buck” in terms of download speed due to its streamlined approach. TCP offers rock-solid stability and is beneficial if you experience packet loss or inconsistent connectivity.
Why UDP is the Best Option for Torrenting
For most torrenting scenarios, UDP reigns supreme. Here’s why it’s often the default and recommended choice in VPN clients:
Speed is King: UDP’s streamlined nature minimizes overhead compared to TCP. This lean protocol prioritizes quickly sending data, resulting in faster downloads, especially when grabbing large files.
Robust Protection: While UDP does not offer TCP’s meticulous error correction, torrenting protocols have built-in mechanisms to verify file integrity. This ensures your files arrive complete and uncorrupted, making UDP’s speed the clear winner.
Bottom Line
Unless you encounter specific issues (which we’ll address next), UDP is the way to go for optimal torrent download performance, while still benefiting from solid protection.
When TCP Might Be Necessary
While UDP offers the fastest connection, there are a few scenarios where TCP can be a lifesaver:
Censorship and Port Blocking: Some countries or ISPs (Internet Service Providers) actively monitor and block UDP traffic to discourage VPN use. If you find yourself unable to connect to your VPN over UDP, switching to TCP might bypass these restrictions, as its traffic can blend in with regular web browsing more easily.
Unreliable Connections: If your internet connection is prone to packet loss (data packets getting lost in transit), UDP can struggle. TCP’s error-correction mechanisms ensure that every bit of your torrent downloads successfully, even if it takes a bit longer.
Slow Speeds Prioritize Stability: On extremely slow connections, TCP’s reliability becomes more appealing than UDP’s raw speed. A stable, consistent download often beats a faster one that keeps stalling.
How to Switch Between UDP and TCP in Your VPN
The good news is that most reputable VPN providers offer both UDP and TCP protocols, giving you the flexibility to optimize your torrenting experience. Here’s the general process, followed by specific steps for two of our favorite VPNs for torrenting.
General Steps:
Keep in mind that the exact menus and wording might vary between VPNs, but the core concept remains the same.
- Open Your VPN Settings: Look for a gear icon, a “Settings” menu, or sometimes an “Advanced” tab within your VPN client.
- Locate the Protocol Option: It’s often under “Protocol,” “Connection Type,” or something similar.
- Choose Your Protocol: You should see a dropdown menu or toggle to switch between them.
- Save and Reconnect: Apply your changes and reconnect your VPN to start using the new protocol.
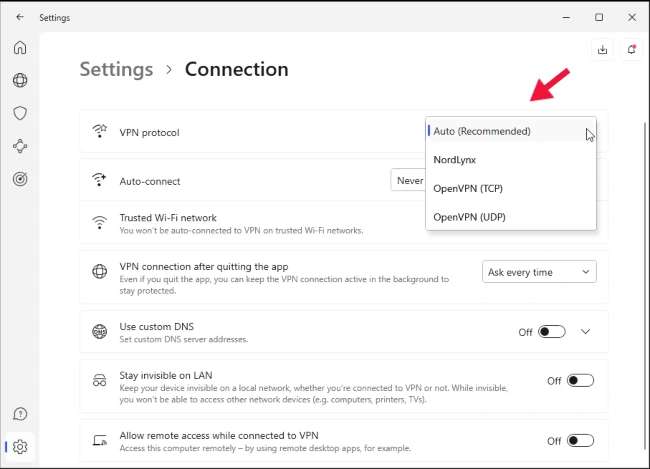
Example 1: NordVPN
As you can see, finding this option in the NordVPN application is very easy. You just go to “Settings” > “Connection” > “VPN Protocol“.
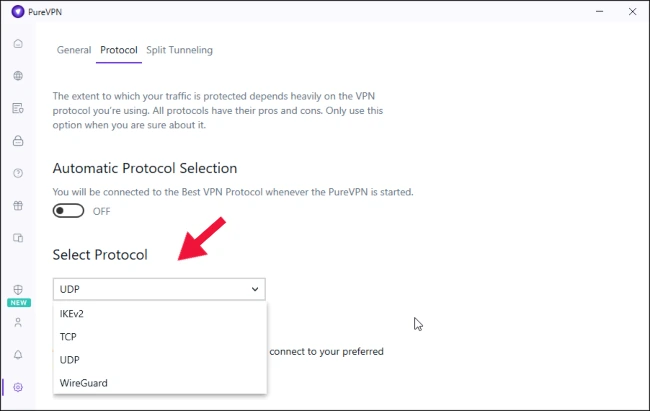
Example 2: PureVPN
In the case of PureVPN, it’s as simple as going to “Settings” > “Protocol“.
Looking Beyond the Protocol
As a note of caution, before immediately blaming the protocol for slow downloads, remember that other factors can significantly impact file-sharing performance. These include your VPN server selection, torrent client settings, and underlying internet connection quality.
You can get a deeper insight into optimizing all these aspects in our tutorial on how to speed up torrent downloads.
Conclusion
When it comes to optimizing your torrenting experience with the OpenVPN protocol, UDP is the best way to maximize speed. However, remember that TCP is your trusty backup plan when facing connection issues, censorship, or unreliable internet.
The best part? You have the power to experiment! Try both protocols and see which delivers the most reliable results for your specific setup.